Cfa Level 1 Formulas Pdf
144 Cards in this Set
Study Flashcards On CFA level 1 formulas at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. /cricket-2005-game-download.html. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want! Register today to get free access to our CFA Level 1 question bank. AnalystPrep also features QBanks and Study Notes for CFA Level 2&3 and FRM part 1&2. Nov 13, 2014 CFA formula approach (Originally Posted: ) Can any recent Level 1 examinees share what formulas or topics they did/did not/wish they had memorize(d) for the exam? In the midst of prepping my formula sheet now. I'm imagining that for example memorizing the formula for excess kurtosis will not be worth my time/brainspace. CFA Level 1 (2019) - Complete Financial Reporting & Analysis 4.5 (1,253 ratings) Course Ratings are calculated from individual students’ ratings and a variety of other signals, like age of rating and reliability, to ensure that they reflect course quality fairly and accurately. A clear and personalized study plan is here! Schweser's upgraded content and redesigned study platform are exactly what you need to pass the Level I exam. 101pgL2FormulaBooklet.pdf Once you master these, you ace the exam! This is a 2019 formula booklet. Bonus: it's genuine handwritten, to have a lasting impact on your mind. Required CFA® Institute disclaimer: 'CFA® Institute does not endor.
Sep 09, 2017 Pepakura Designer is an authoritative yet very humble and easy-to-use software program, permits you to easily make 2D patterns from the 3D models. It proposals the calmest solution to make patterns from your standing 3D design. The program supports a wide variety of 3D design formats; you will need simply to import designs from AutoCAD, Google Earth, Lightwave, 3D Studio, and many other. Pepakura Designer is the English version of paper craft software 'Pepakura Designer' developed in Japan. Pepakura Designer allows you to create a development for paper craft easily from 3D data. The latest version is 4.1.6. 29 May 2019 Pepakura Designer 4.1.6 has been released. Pepakura designer mac.
- Front
- Back
=Inflation adjusted Par Value X (Stated coupon rate/2) | |
=Yield on bond with Higher yield - Yield on bond with lower yield | |
[(1 + one year forward rate at time 0)(1 + one year forward rate at time 1)(1 + one year forward rate at time 2)^1/3] - 1 | |
1 year forward rate at time 2 and 7 year forward rate at time 3 | =[(Spot rate at time 3)^3 / (Spot rate at time 2)^2] - 1 and ={[(1 + 10 year spot rate)^10 / (1 + 3 year spot rate)^3]^1/7} - 1 = |
=(Bond price when yield falls - bond price when yield rise) / 2 X initial price X % change in yield as decimal | |
=Duration effect + convexity effect = [(-duration x change in yield)+ (convexity X change in yield^2)] X 100 | |
=duration X .0001 X bond value Note: if rates increase, bond value must fall. After calculation, use this information for come up with final answer | |
=notional principal X [(floating rate-forward rate)X(days to maturity/360) / (1 + floating rate)X(days to maturity/360) | |
Lower = Max[0,(X/(1+RFR)^T-t) - S] Upper = (X/(1+RFR)^T-t) | |
= (SWAP fixed rate - LIBOR) X (Days to maturity/360) X (Notional Principal) | |
= Cov1,2/SD1 X SD2 Indicates strength and direction in which two random variables move together. | |
Depreciation in year X = (original cost-salvage value)(n-x+1)/SYD | |
=Current assets - inventories/Current Liabilities or =Cash + mkt. Securities + receivables / current liabilities | |
=(Avg. Rec. collection period) + (Avg. Inventory processing period) - (Payables payment period) | |
=Operating Profit / Net Sales or EBIT / Net Sales | |
=Net Income + Interest Exp. / Avg. Total Capital | |
=Net Income - Preferred Dividends / Avg. Common equity | |
=SD of EBIT / Mean of EBIT or SD of Operating Income / Mean of operating income | |
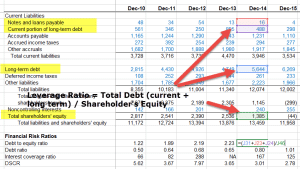
=Total long term debt / Total Equity or Long term liabilities + Deferred Tax + PV of lease obligations / Common + Preferred Equity | |
=Current Liabilities + Long term debt / Total Debt + Total Equity | |
=CFO + Interest expense + ELIE / Interest Expense + ELIE | |
=CFO / Total long term debt + current interest bearing liabilities | |
=Total Asset Turnover X Equity Multiplier X Net profit Margin or =Sales/Total Assets X Net Income/Sales X Assets/Equity | |
=[(EBIT/Sales)(Sales/Assets)-(Int. Exp/Assets)](assets/equity)(1-t) | |
=(Net Income - Preferred Dividend) / (Weighted Avg. # common shares outstanding) | |
=(Net Income - Pref Div)+(Conv. Pref. Div.)+(Conv. Debt int.)(1-t) / (Weighted Avg. # Common)+(Conv. Pref Shares)+(Conv. debt shares)+(shares issued for Stock Options) | |
=LIFO COGS - (Ending LIFO Reserve - Beg. LIFO Reserve) | |
=Accumulated Depreciation / Depreciation Expense | |
=Accumulated Depreciation / Ending Gross Investment | |
=(Market rate @ issuance) X (Balance Sheet Value of Liability at begenning of period) | |
=Real Risk Free Rate + Expected inflation or =(1+RFRreal)X(1+inflation premium)-1 | |
=(Real Risk Free Rate + Expected inflation) + Default risk premium + Liquidity premium + Maturity Risk Premium or =[(1+RFR)(1+IP)(1+RP)]-1 | |
=(Face Value-Purchase Price/Face Value) X (360/t) | |
= 90% CI = -1.65<X<1.65 = 95% CI = -1.96<X<1.96 = 99% CI = -2.58<X<2.58 | |
=Observation-population mean / Standard Deviation | |
= Potential deposit expansion multiplier X Increase in excess reserves | |
= Money Supply X Velocity = GDP = PRICE X Real Output | |
= % change in Qunatity Demanded / % change in Price | |
= % change in Quantity demanded / % change in income | |
= [(MP of A)/Price A] = [(MP of B)/Price B] = [(MP of C)/Price C] | |
=Current Account + Financial Account + Reserve Account = 0 | |
=Expected future exchange rate = Spot Rate X [((1+inflation domestic)^t) / ((1+inflation foreign)^t)] | |
=Outstanding short interest / Avg daily volume on exchange note: ratio high (6 or above), potential demand, bullish - ratio low (4 or below), potential for short sales. bearish sign. | |
=# block uptick transactions / # block downtick transactions note: Bullish if ratio close to .7. Bearish if ratio close to 1.1 | |
=Quality bond yield / average bond yields note: Periods of confidence yield spreads narrow, CI GETS BIGGER - Periods of pessimism yield spreads widen, CI GETS SMALLER | |
Confidence index Tbill-Eurodollar spread Specialist short sales Debit balances in brokerage accounts | |
=Short sales by specialists / Total short sales on NYSE note: below 30% bullish - above 50% bearish | |
=Mutual fund cash / total fund assets note: greater than 13%, funds holding cash and market is bearish, CONTRARY BULLISH - Vice versa if less than 5% | |
Mutual fund ratio Investor credit balances in brokerage accounts Investment advisor opinions OTC vs. NYSE volume CBOE Put/call ratio Stock index futures | |
=Bullish opinions / total opinions note: Greater than 60%, mkt bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH - Less than 20%, mkt bullish, CONTRARIAN BEARISH | |
=OTC volume / NYSE volume note: Greater than 112%, speculation high, CONTRARIAN BEARISH - less than 87%, investors bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH | |
=Puts/Calls note: Greater than .5, mkt bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH - less than .35, mkt bullish, CONTRARIAN BEARISH | |
=Retention rate X ROE or (1-dividend payout) X ROE | |
Tail points toward negative number/origin. If median is higher than mean, distribution is negatively skewed | |
Distribution with negative excess kurtosis Distribution is less peaked than normal distribution | |
Things to consider in determining DTL treated as equity | 1. Likelihood of reversal 2. Growth rate of entity 3. Time Value of money |
Ratio fo debt and comm0n/preferred equity that creates lowest possible WACC and maximizes the value of the firms stock |
144 Cards in this Set
Cfa Level 1 All Formulas
- Front
- Back
Cfa Level 1 Formula Sheet 2017 Pdf Free
=Inflation adjusted Par Value X (Stated coupon rate/2) | |
=Yield on bond with Higher yield - Yield on bond with lower yield | |
[(1 + one year forward rate at time 0)(1 + one year forward rate at time 1)(1 + one year forward rate at time 2)^1/3] - 1 | |
1 year forward rate at time 2 and 7 year forward rate at time 3 | =[(Spot rate at time 3)^3 / (Spot rate at time 2)^2] - 1 and ={[(1 + 10 year spot rate)^10 / (1 + 3 year spot rate)^3]^1/7} - 1 = |
=(Bond price when yield falls - bond price when yield rise) / 2 X initial price X % change in yield as decimal | |
=Duration effect + convexity effect = [(-duration x change in yield)+ (convexity X change in yield^2)] X 100 | |
=duration X .0001 X bond value Note: if rates increase, bond value must fall. After calculation, use this information for come up with final answer | |
=notional principal X [(floating rate-forward rate)X(days to maturity/360) / (1 + floating rate)X(days to maturity/360) | |
Lower = Max[0,(X/(1+RFR)^T-t) - S] Upper = (X/(1+RFR)^T-t) | |
= (SWAP fixed rate - LIBOR) X (Days to maturity/360) X (Notional Principal) | |
= Cov1,2/SD1 X SD2 Indicates strength and direction in which two random variables move together. | |
Depreciation in year X = (original cost-salvage value)(n-x+1)/SYD | |
=Current assets - inventories/Current Liabilities or =Cash + mkt. Securities + receivables / current liabilities | |
=(Avg. Rec. collection period) + (Avg. Inventory processing period) - (Payables payment period) | |
=Operating Profit / Net Sales or EBIT / Net Sales | |
=Net Income + Interest Exp. / Avg. Total Capital | |
=Net Income - Preferred Dividends / Avg. Common equity | |
=SD of EBIT / Mean of EBIT or SD of Operating Income / Mean of operating income | |
=Total long term debt / Total Equity or Long term liabilities + Deferred Tax + PV of lease obligations / Common + Preferred Equity | |
=Current Liabilities + Long term debt / Total Debt + Total Equity | |
=CFO + Interest expense + ELIE / Interest Expense + ELIE | |
=CFO / Total long term debt + current interest bearing liabilities | |
=Total Asset Turnover X Equity Multiplier X Net profit Margin or =Sales/Total Assets X Net Income/Sales X Assets/Equity | |
=[(EBIT/Sales)(Sales/Assets)-(Int. Exp/Assets)](assets/equity)(1-t) | |
=(Net Income - Preferred Dividend) / (Weighted Avg. # common shares outstanding) | |
=(Net Income - Pref Div)+(Conv. Pref. Div.)+(Conv. Debt int.)(1-t) / (Weighted Avg. # Common)+(Conv. Pref Shares)+(Conv. debt shares)+(shares issued for Stock Options) | |
=LIFO COGS - (Ending LIFO Reserve - Beg. LIFO Reserve) | |
=Accumulated Depreciation / Depreciation Expense | |
=Accumulated Depreciation / Ending Gross Investment | |
=(Market rate @ issuance) X (Balance Sheet Value of Liability at begenning of period) | |
=Real Risk Free Rate + Expected inflation or =(1+RFRreal)X(1+inflation premium)-1 | |
=(Real Risk Free Rate + Expected inflation) + Default risk premium + Liquidity premium + Maturity Risk Premium or =[(1+RFR)(1+IP)(1+RP)]-1 | |
=(Face Value-Purchase Price/Face Value) X (360/t) | |
= 90% CI = -1.65<X<1.65 = 95% CI = -1.96<X<1.96 = 99% CI = -2.58<X<2.58 | |
=Observation-population mean / Standard Deviation | |
= Potential deposit expansion multiplier X Increase in excess reserves | |
= Money Supply X Velocity = GDP = PRICE X Real Output | |
= % change in Qunatity Demanded / % change in Price | |
= % change in Quantity demanded / % change in income | |
= [(MP of A)/Price A] = [(MP of B)/Price B] = [(MP of C)/Price C] | |
=Current Account + Financial Account + Reserve Account = 0 | |
=Expected future exchange rate = Spot Rate X [((1+inflation domestic)^t) / ((1+inflation foreign)^t)] | |
=Outstanding short interest / Avg daily volume on exchange note: ratio high (6 or above), potential demand, bullish - ratio low (4 or below), potential for short sales. bearish sign. | |
=# block uptick transactions / # block downtick transactions note: Bullish if ratio close to .7. Bearish if ratio close to 1.1 | |
=Quality bond yield / average bond yields note: Periods of confidence yield spreads narrow, CI GETS BIGGER - Periods of pessimism yield spreads widen, CI GETS SMALLER | |
Confidence index Tbill-Eurodollar spread Specialist short sales Debit balances in brokerage accounts | |
=Short sales by specialists / Total short sales on NYSE note: below 30% bullish - above 50% bearish | |
=Mutual fund cash / total fund assets note: greater than 13%, funds holding cash and market is bearish, CONTRARY BULLISH - Vice versa if less than 5% | |
Mutual fund ratio Investor credit balances in brokerage accounts Investment advisor opinions OTC vs. NYSE volume CBOE Put/call ratio Stock index futures | |
=Bullish opinions / total opinions note: Greater than 60%, mkt bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH - Less than 20%, mkt bullish, CONTRARIAN BEARISH | |
=OTC volume / NYSE volume note: Greater than 112%, speculation high, CONTRARIAN BEARISH - less than 87%, investors bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH | |
=Puts/Calls note: Greater than .5, mkt bearish, CONTRARIAN BULLISH - less than .35, mkt bullish, CONTRARIAN BEARISH | |
=Retention rate X ROE or (1-dividend payout) X ROE | |
Tail points toward negative number/origin. If median is higher than mean, distribution is negatively skewed | |
Distribution with negative excess kurtosis Distribution is less peaked than normal distribution | |
Things to consider in determining DTL treated as equity | 1. Likelihood of reversal 2. Growth rate of entity 3. Time Value of money |
Ratio fo debt and comm0n/preferred equity that creates lowest possible WACC and maximizes the value of the firms stock |